Voltage Regulators –Guardians for High Quality Power Distribution – In an electric power distribution system, voltage regulators may be installed at a substation (1p/3p) or along distribution lines/feeders (1p) so that all customers receive steady voltage independent of how much power is drawn from the line. The distribution automation portion of the VR market is primarily for automated control of single-phase units installed along MV distribution lines. In both distribution feeder and substation applications, VRs are often paired with power capacitors.
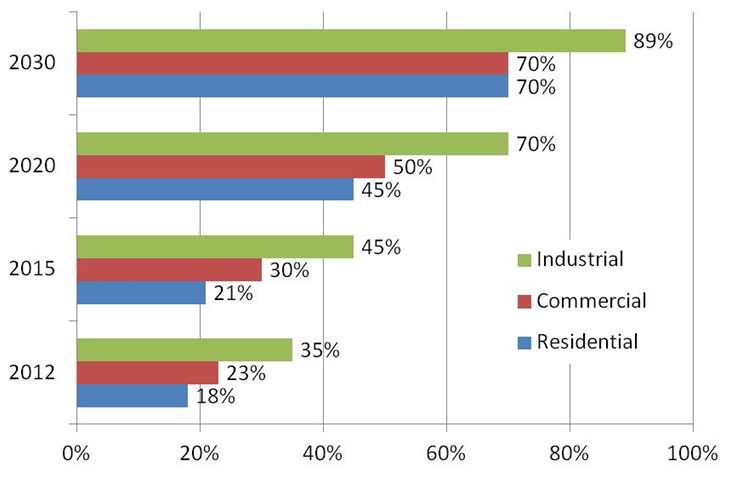
Currently the single most important factor behind the growth in use of single-phase VRs is the increase in installations of distributed energy resources (DERs) and the impact that these grid-connected resources are having on grid voltage stability. Because of the variable or intermittent nature of DERs, there is a need to control voltage fluctuations, hence the push to utilize more VRs by utilities that are actively involved with DERs in their service territories. New construction of C&I sites, residential developments in the suburbs as well as feeder length in large rural areas are also key factors affecting the increase in use of VRs. Certain regulatory actions in place or planned will continue to influence the need for VRs. See the chart just below for a look at key drivers for using VRs among IOUs, Public Utilities and electric power cooperatives.
Click on chart to enlarge!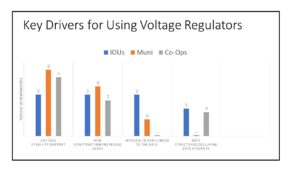 Keep in mind that the nation’s electric power delivery/distribution system was designed for one-way (or uni-directional) power flow, and with the development of DERs, we are confronted with a need to accommodate two-way (bi-directional) power flows. This changes the feeder voltage profile making voltage regulation more challenging, with DERs tending to cause local voltage rise along a distribution feeder. The expansion of variable renewable generation resources owned by industrial/commercial companies will mean growth in the non-utility/C&I portion of the VR market. VRs will continue to be used to control voltage levels from these intermittent resources.
Keep in mind that the nation’s electric power delivery/distribution system was designed for one-way (or uni-directional) power flow, and with the development of DERs, we are confronted with a need to accommodate two-way (bi-directional) power flows. This changes the feeder voltage profile making voltage regulation more challenging, with DERs tending to cause local voltage rise along a distribution feeder. The expansion of variable renewable generation resources owned by industrial/commercial companies will mean growth in the non-utility/C&I portion of the VR market. VRs will continue to be used to control voltage levels from these intermittent resources.
Market Size Summary:
Some suppliers have suggested to Newton-Evans that growth of 10-15% per year is on the horizon. A lot will depend upon continuing economic recovery and the promulgation of DER-friendly policies and regulations being planned over the coming years. Currently, there are three principal manufacturers of automated voltage regulators serving the domestic U.S. market. These are General Electric, Eaton Corporation and Siemens. Together the “Big Three” control about 75-80% of the combined VR market. Howard Industries is next, followed by Schneider Electric, Delta Star and Basler Electric with each having a few dozen important utility customers and together comprise the remaining 20-25% of the VR equipment manufacturing market.
Market Drivers:
Currently the single most important market driver for using VRs is the increasingly important role of distributed energy resources (DERs) and the impact that these resources are having on grid voltage stability. Because of the variable nature of DERs, there is a need to control voltage fluctuations, hence the push to utilize more VRs by utilities that are actively involved with DER in their service territories. New construction of C&I sites and residential developments in the suburbs are also key factors affecting the growth in use of VRs. Feeder length among suburban, exurban and rural areas and some regulatory actions also impact the need for VRs. Perhaps offsetting some of the demand from DER sites will be a new generation of smart inverters that may be able to provide voltage stability from DER sites to the grid interconnection point, perhaps nullifying the need for a separate VR on-site. The publication of IEEE 1547-2018 provides for performance criteria for DERs including such functionality as Volt-Var control which can also be used to help regulate the distribution system.
Operational Driver:
While the use of single-phase VRs can be found among many hundreds of IOUs, public utilities and cooperatives, the use of three phase VRs is less widely used among munis and co-ops. Many of these utilities have switched to using single-phase units where, in the past, they may have used a three-phase unit. There are also about 10-15% of utilities that do not use VRs, but rely on on-load tap changers (OLTCs) with substation transformers – most within urban corridors with relatively short distribution feeders. You may want to return here for more articles on grid modernization over the coming weeks and months.


 summary reviews and highlights from completed studies
summary reviews and highlights from completed studies
