Over the past two years, the pandemic has affected our lives, our businesses and the nation’s plans for infrastructure modernization, including the electric power grid. We had earlier (2020) forecasted rather robust growth in spending on IT, OT and smart grid initiatives in a grid modernization report prepared for a client organization.
During the first year of the pandemic, Newton-Evans conducted a small sample study (25 large and mid-size utilities) of the impact of COVID on electric power transmission and distribution capital investment projects.
Observations from that 2020 study indicated capital investment plans for some utilities had been scaled back by as much as 50% for 2020 and 2021. Other respondents reported that capital projects had been deferred for 12, 24 or even 36 months. A few utilities held fast to their pre-pandemic investment plans as long as they could do so.
In Figure 1, note our belief that total 2021 expenditures for the combination of IT, OT and smart grid projects likely reached about $14.2 Billion. In 2020, Newton-Evans had estimated that 2021 would likely see about $16.1 Billion in these combined expenditures, but by that year, the pandemic had firmly taken hold, restricting the availability of utility workforce personnel. COVID also impacted the manufacturing of some electrical equipment and provision of consulting and engineering services related to IT, OT and grid modernization projects.
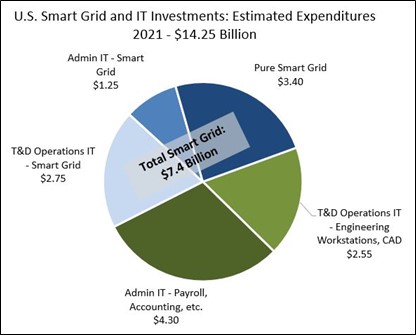
Figure 1.
NOTE: Total IT + OT + SG Expenditures = $14.25 Billion
($5.55 Billion for IT + $5.30 Billion for OT + $3.4 Billion for “pure” Smart Grid)
$14.25 B = about 4.75% of electric utility operating revenue or 3.6% of total electricity sales.
IT spending alone likely less than 2% of operating revenue.
Now, the question arises – What is included in “pure” smart grid investment? Here, we include smart grid devices and equipment that acquire and transmit data and other signals to monitor and/or control utility field operations outside of the substation fence. For the most part, these are 21st century developments or generational improvements over earlier “legacy” devices. Pole top RTUs, distribution line fault indicators and feeder monitors, multiple types of controllers (for capacitor banks, automatic circuit reclosers, voltage regulators, line mounted monitoring devices et al) and automated switches and protective devices).
The related advanced communications infrastructure including built-out portions of the utility wide-area networks, local area networks and supporting infrastructure for automatic metering equipment are also placed in the “pure” smart grid bucket. IT system components related to smart grid are typified by meter data management systems, the customer services links to outage management systems, and geographic information systems to name a few. Operations side systems and applications would include advanced distribution management systems which collect and aggregate the thousands of field data points now configured with intelligent electronic field devices mentioned earlier that assist in more effective operation of the distribution grid.
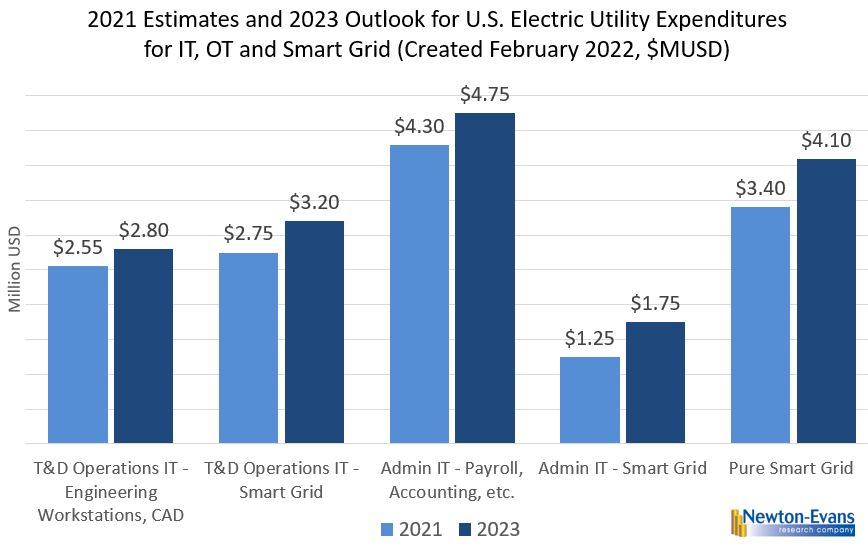
By the third quarter of 2021, some recovery in capital spending for transmission and distribution was underway, based on recent discussions with a variety of industry sources. Even now, in the first quarter of 2022, we are still in a cautionary progression, given the lingering concerns over, and the effects of the OMICRON variant on the utility labor force and on delays in equipment availability in some situations. By 2023, I anticipate combined investment in IT, OT and grid modernization projects as shown in Figure 3 below will increase to more than $16.6 Billion. When compared with a pre-pandemic outlook calling for about $19.2 Billion in such investment in the coming year this leaves a shortfall of $2.6 Billion.
Importantly, when utilities have been compared with other industries related to IT spending, at first glance the industry appears to invest relatively less of its revenues in IT and OT. However, we have found that even in this pandemic area, with total U.S. electric power revenues approaching $400 Billion, the investment in combined IT and OT, plus related portions of grid modernization technology projects (exclusive of the cost of grid modernization equipment), the level of capital spending for grid modernization is closer to the 3.6% – 4.0% investment level. IT spending alone hovers around 1.5%-1.9% of operating revenues. Adding in the industry’s investment in OT and in key technology aspects of smart grid projects, the relative investment in overall information technology in total climbs to a much more reasonable level. See Figure 2.
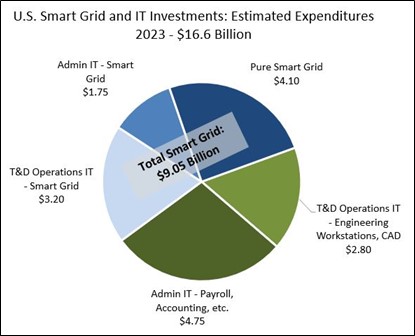
Figure 2.
Two key assumptions about this outlook:
1. COVID will be endemic, not pandemic, by 3Q 2022.
2. Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act actually begins funding significant portions of the $72.3 Billion allocated for energy and electric power infrastructure renewal by mid-year 2022.
The impact of COVID on electric power industry investment during 2020 and 2021 and into 2022 has taken its toll. The question facing the industry and the nation is whether or not this estimated $16.5 Billion shortfall in grid modernization investment (as postponed or deferred from initial estimates) can be made up during the remaining years of this decade? My belief is that the investment gap will be narrowing over the next 36 months, as shown in Figure 3 below, and the pre- and post-pandemic trendlines will indeed converge in the latter years of the 2020’s. Closing the investment gap will especially be likely – and may occur earlier than anticipated with help from DOE funding. Much will depend on federal funds flows from the recently enacted Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act – legislation that will enable additional billions of dollars to be provided for grid modernization programs and related energy projects. At least several billion dollars of the $72 billion or so earmarked for electric power modernization will be applied to IT, OT and “pure” smart grid projects, although the majority of the total budget is earmarked for transmission grid expansion, overall grid hardening and integration of renewable energy sources.
I believe that this forthcoming federal investment in the nation’s electric power grid – coupled with the investments of the nation’s utilities, must include funding for research and development of advanced technical solutions for ever higher levels of cybersecurity and grid resilience.
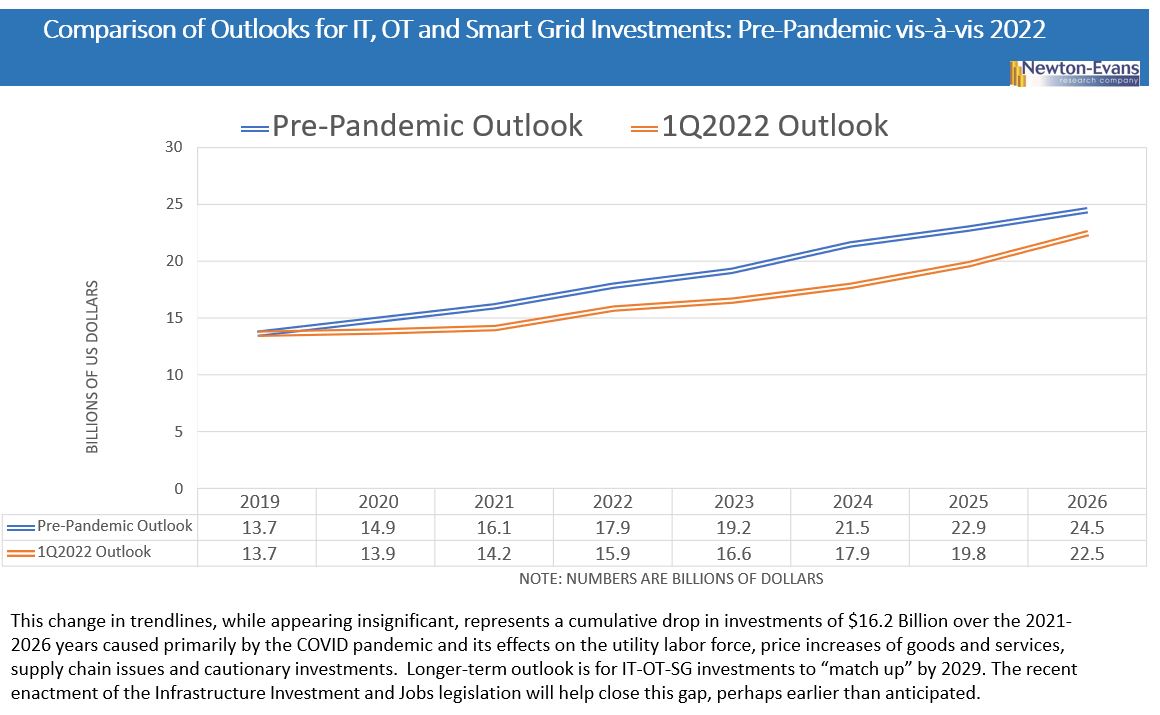
As of February 2022, the nation’s electric utilities are re-starting or initiating a number of grid modernization projects and programs, deferred in part over the past 24 months. This activity will help boost IT, OT and smart grid device/equipment expenditures this year and into 2023. Figure 4 illustrates the near-term growth estimate we have made for the IT, OT and smart grid field components of capital investment as the effects of the COVID pandemic begin to wane in the first quarter of 2022.

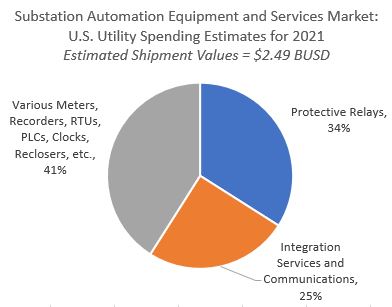
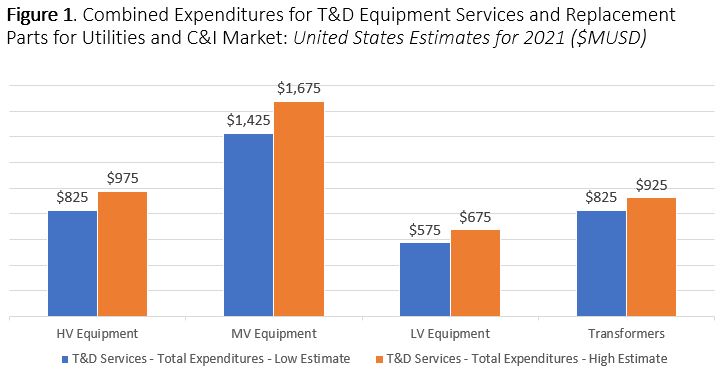
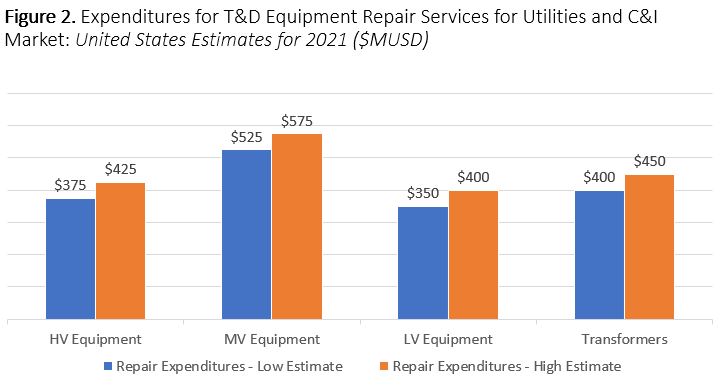
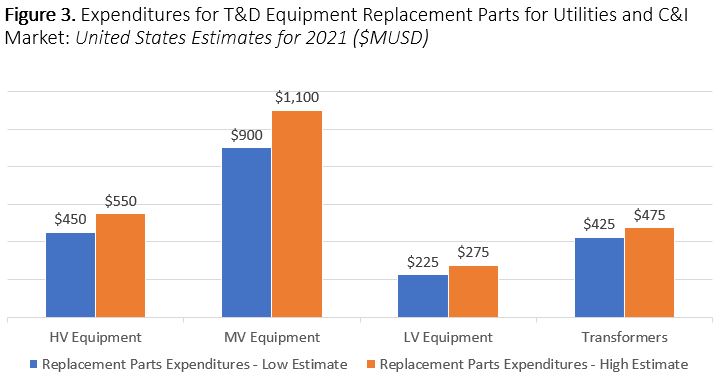




 summary reviews and highlights from completed studies
summary reviews and highlights from completed studies
